# Hybrid Search
NOTE
This guide is only applicable to the DB version 1.5.0 or higher.
This guide explains how to perform full-text and vector hybrid search in MyScale.
Full-text search and vector search each have their own strengths and weaknesses. Full-text search is suitable for basic keyword retrieval and text matching, while vector search excels at cross-document semantic matching and deep understanding of semantics but may lack efficiency with short text queries. To leverage the benefits of both approaches, hybrid search was developed. By combining full-text indexing and vector search characteristics, it can address various text search requirements effectively, enhance accuracy and speed in searching texts, and fulfill users' expectations for precise results efficiently.
# Tutorial Overview
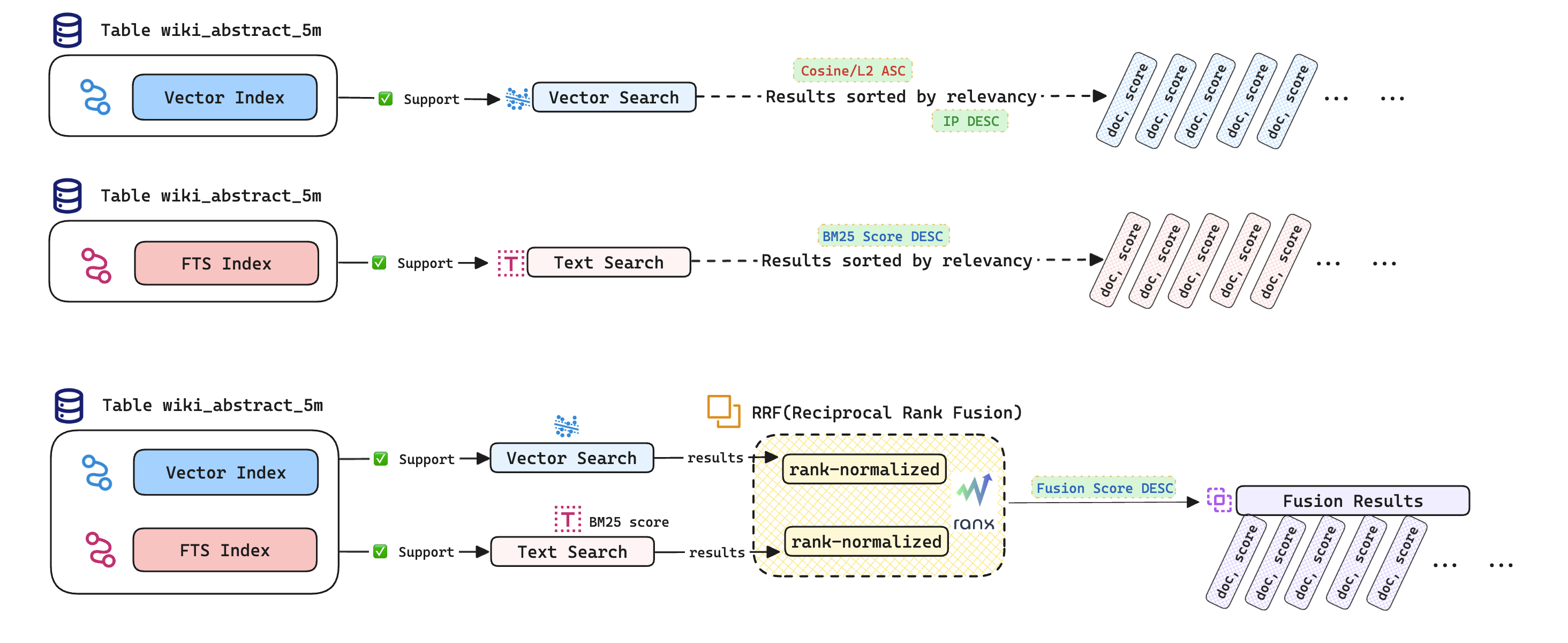
This document will guide you through three search experiments:
All document and query texts utilize the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 (opens new window) model for vector generation and Cosine distance for similarity measurement.
MyScale integrates the Tantivy (opens new window) library to enable the BM25 indexing for full-text search (FTS). By indexing all textual data in the table, MyScale's FTS capability allows search results to be ranked based on BM25 scores, providing more relevant and accurate search experiences.
✅ Fusing Vector and Text Search Results using RRF Strategy
We employ the widely-used Python library ranx (opens new window) to combine vector search and text search outcomes. This fusion enhances the adaptability of text searches across various scenarios, ultimately improving search accuracy.
Before starting, ensure you have a MyScale cluster set up. For setup instructions, refer to our Quickstart Guide (opens new window).
# Dataset
The experiment utilized the Wikipedia abstract dataset (opens new window) provided by RediSearch, comprising 5,622,309 document entries. The text was processed using the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 (opens new window) model to create 384-dimensional vectors stored in the body_vector column. Similarity between vectors was calculated using cosine distance.
TIP
For more information on how to use all-MiniLM-L6-v2, please refer to HuggingFace's documentation.
The dataset wiki_abstract_with_vector.parquet (opens new window) has a size of 8.2GB. You can preview its contents below without needing to download it locally since we will import it directly into MyScale via S3 in subsequent experiments.
| id | body | title | url | body_vector |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 77 | Jake Rodkin is an American .... and Puzzle Agent. | Jake Rodkin | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jake_Rodkin (opens new window) | [-0.081793934,....,-0.01105572] |
| 78 | Friedlandpreis der Heimkehrer is ... of Germany. | Friedlandpreis der Heimkehrer | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Friedlandpreis_der_Heimkehrer (opens new window) | [0.018285718,...,0.03049711] |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
# Table Creation and Data Import
To create the table wiki_abstract_5m in MyScale's SQL workspace, execute the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE default.wiki_abstract_5m(
`id` UInt64,
`body` String,
`title` String,
`url` String,
`body_vector` Array(Float32),
CONSTRAINT check_length CHECK length(body_vector) = 384
)
ENGINE = MergeTree
ORDER BY id
SETTINGS index_granularity = 128;
Import data from S3 into the table. Please be patient during the data import process.
INSERT INTO default.wiki_abstract_5m
SELECT * FROM s3('https://myscale-datasets.s3.ap-southeast-1.amazonaws.com/wiki_abstract_with_vector.parquet', 'Parquet');
Note
The estimated time for data import is approximately 10 minutes.
Verify if there are 5,622,309 rows of data in the table by running this query:
SELECT count(*) FROM default.wiki_abstract_5m;
Output:
| count() |
|---|
| 5622309 |
For optimizing the table to enhance vector search performance by merging its data parts into one part (optional), execute this SQL command in your SQL workspace:
OPTIMIZE TABLE default.wiki_abstract_5m FINAL;
This optimization step may require some time to complete.
Check whether the data parts of this table have been compressed into a single part with this query:
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM system.parts WHERE table='wiki_abstract_5m' AND active=1;
If successful, you will see:
| count() |
|---|
| 1 |
# Build Index
# Create FTS Index
TIP
To learn how to create an FTS index, please consult the FTS index documentation.
When setting up an FTS index, users have the option to customize the tokenizer. In this example, the stem tokenizer is utilized along with applying stop words. The stem tokenizer can overlook word tenses in text for more precise search outcomes. By using stop words, common words like "a," "an," "of," and "in" are filtered out to enhance search accuracy.
ALTER TABLE default.wiki_abstract_5m
ADD INDEX body_idx (body)
TYPE fts('{"body":{"tokenizer":{"type":"stem", "stop_word_filters":["english"]}}}');
Execute materialization of the index:
ALTER TABLE default.wiki_abstract_5m MATERIALIZE INDEX body_idx;
# Create Vector Index
TIP
Learn more about the MSTG vector index in the vector search documention.
To build the MSTG vector index using Cosine as the distance calculation method for the body_vec_idx on the table default.wiki_abstract_5m, execute this SQL statement:
ALTER TABLE default.wiki_abstract_5m
ADD VECTOR INDEX body_vec_idx body_vector
TYPE MSTG('metric_type=Cosine');
Constructing a vector index can be time-consuming. To monitor its progress, run this SQL query. If the status column shows "Built," it means that the index has been successfully created. While still in progress, it should display "InProgress."
SELECT * FROM system.vector_indices;
# Perform Hybrid Search
# Preliminary Preparations
To convert the query text into vectors, we will utilize the all-MiniLM-L6-v2 (opens new window) model.
Firstly, install the sentence-transformers library by running:
pip install -U sentence-transformers
For the fusion stage, we will employ the ranx (opens new window) library. Install it using:
pip install -U ranx
The hybrid search practice will be implemented in a Python file. Before proceeding with this practice, ensure to input your MyScale cluster information into the provided example code.
TIP
You can find the connection details for a MyScale cluster in the Web console.
import clickhouse_connect
from numba import NumbaTypeSafetyWarning
from prettytable import PrettyTable
from ranx import Run, fuse
from ranx.normalization import rank_norm
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore', category=NumbaTypeSafetyWarning)
# Use transfromer all-MiniLM-L6-v2
model = SentenceTransformer('sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2')
# MyScale information
host = "your cluster end-point"
port = 443
username = "your user name"
password = "your password"
database = "default"
table = "wiki_abstract_5m"
# Init MyScale client
client = clickhouse_connect.get_client(host=host, port=port,
username=username, password=password)
# Use a table to output your content
def print_results(result_rows, field_names):
x = PrettyTable()
x.field_names = field_names
for row in result_rows:
x.add_row(row)
print(x)
# Execute Vector Search
TIP
The British Graham Land expedition (BGLE) was a British expedition. For detailed information about them please refer to Wikipedia (opens new window).
We aim to identify the locations visited and mapped by the BGLE expedition in this dataset. To do so, we will use "Charted by BGLE" as the search string when conducting a vector search query.
TIP
Please include the example code provided in this message into the Python file that was created during the previous preparation work to ensure smooth execution of the program. Additionally, make sure to handle other steps in a similar manner.
terms = "Charted by BGLE"
terms_embedding = model.encode([terms])[0]
vector_search = f"SELECT id, title, body, distance('alpha=3')" \
f"(body_vector,{list(terms_embedding)}) AS distance FROM {database}.{table} " \
f"ORDER BY distance ASC LIMIT 100"
vector_search_res = client.query(query=vector_search)
print("\nVectorSearch results:")
print_results(vector_search_res.result_rows[:10], ["ID", "Title", "Body", "Distance"])
The documents retrieved through vector search do not contain any information related to "Charted by BGLE" in the top 10 results, as vector search tends to perform poorly for short text queries.
| ID | Title | Body | Distance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1177089 | B.G. discography | This is the discography of B.G. | 0.44516414403915405 |
| 2710950 | Ruy Blas and the Blasé Roué | Ruy Blas and the Blasé Roué is a burlesque written by A. C. | 0.4736078381538391 |
| 4571962 | BLL | BLL may refer to: | 0.48070353269577026 |
| 3797998 | Bles | Bles may refer to: | 0.4849556088447571 |
| 4558187 | The Complete Blam Blam Blam | The Complete Blam Blam Bam is a compilation LP by Blam Blam Blam. It was released on November, 1992. | 0.4863016605377197 |
| 5556733 | BLG | BLG may refer to: | 0.49544525146484375 |
| 4591273 | Blagg | Blagg may refer to: | 0.5007722973823547 |
| 3087541 | Paul Bley discography | This is the discography for Canadian jazz musician Paul Bley. | 0.5030192136764526 |
| 3389086 | Blot (album) | Blot is the fourth full-length album by the Norwegian black/Viking metal band Einherjer. It was released on 21 November 2003 by Tabu Recordings. | 0.5040180087089539 |
| 1876940 | Blåljus! | Blåljus! is a six-volume light pocket series of novels by Margit Sandemo and published by the Swedish subsidiade Boknöje AB of the Norwegian publication Bladkompaniet in year 2004. | 0.5080643892288208 |
# Execute Text Search
We utilize MyScale's TextSearch() function to retrieve a set of relevant results along with BM25 scores. To facilitate result fusion later on, we must first store this document data temporarily.
text_search = f"SELECT id, title, body, TextSearch(body, '{terms}') AS score " \
f"FROM {database}.{table} " \
f"ORDER BY score DESC LIMIT 100"
text_search_res = client.query(query=text_search)
# Temporarily store search results.
stored_data = {}
for row in vector_search_res.result_rows:
stored_data[str(row[0])] = {"title": row[1], "body": row[2]}
for row in text_search_res.result_rows:
if str(row[0]) not in stored_data:
stored_data[str(row[0])] = {"title": row[1], "body": row[2]}
# Use Reciprocal Rank Fusion to Fuse Vector and Text Search Results
We utilize the ranx (opens new window) library to combine vector and text search results, implementing the RRF fusion strategy (Reciprocal Rank Fusion) to enhance search accuracy. For alternative fusion strategies, you can consult ranx/fusion (opens new window).
# Extract id and score from query results.
bm25_dict = {"query-0": {str(row[0]): float(row[3]) for row in text_search_res.result_rows}}
# For ranx library, a higher score is expected to indicate greater relevance,
# thus preprocessing is required for vector distance calculation methods such as Cosine and L2.
max_value = max(float(row[3]) for row in vector_search_res.result_rows)
vector_dict = {"query-0": {str(row[0]): max_value - float(row[3]) for row in vector_search_res.result_rows}}
# Normalize query results score.
vector_run = rank_norm(Run(vector_dict, name="vector"))
bm25_run = rank_norm(Run(bm25_dict, name="bm25"))
# Fusion query results using RRF.
combined_run = fuse(
runs=[vector_run, bm25_run],
method="rrf",
params={'k': 10}
)
print("\nFusion results:")
pretty_results = []
for id_, score in combined_run.get_doc_ids_and_scores()[0].items():
if id_ in stored_data:
pretty_results.append([id_, stored_data[id_]["title"], stored_data[id_]["body"], score])
print_results(pretty_results[:10], ["ID", "Title", "Body", "Score"])
The fusion query results are as follows: Hybrid search accurately matched five articles related to the locations charted by the BGLE expedition, showcasing the benefits of hybrid search for processing short text queries.
| ID | Title | Body | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200245 | Salmon Island | Salmon Island () is the westernmost of the Fish Islands, lying off the west coast of Graham Land. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. | 0.09090909090909091 |
| 1177089 | B.G. discography | This is the discography of B.G. | 0.09090909090909091 |
| 5024941 | Woozle Hill | Woozle Hill () is a hill near the center of Galindez Island, in the Argentine Islands in the Wilhelm Archipelago. First charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. | 0.08333333333333333 |
| 2710950 | Ruy Blas and the Blasé Roué | Ruy Blas and the Blasé Roué is a burlesque written by A. C. | 0.08333333333333333 |
| 4571962 | BLL | BLL may refer to: | 0.07692307692307693 |
| 4426976 | Symington Islands | Symington Islands () is a group of small islands lying west-northwest of Lahille Island, in the Biscoe Islands. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. | 0.07692307692307693 |
| 3797998 | Bles | Bles may refer to: | 0.07142857142857142 |
| 197443 | Tadpole Island | Tadpole Island () is an island just north of Ferin Head, off the west coast of Graham Land. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. | 0.07142857142857142 |
| 202128 | Sohm Glacier | Sohm Glacier () is a glacier flowing into Bilgeri Glacier on Velingrad Peninsula, the west coast of Graham Land. Charted by the British Graham Land Expedition (BGLE) under Rymill, 1934-37. | 0.06666666666666667 |
| 4558187 | The Complete Blam Blam Blam | The Complete Blam Blam Bam is a compilation LP by Blam Blam Blam. It was released on November, 1992. | 0.06666666666666667 |
# Conclusion
This document provides insights into the usage of MyScale hybrid search in text search scenarios, focusing on methods and techniques for searching unstructured text data. In the practical exercise, we developed an example using Wikipedia abstracts. Performing hybrid search is easy with MyScale's advanced full-text and vector search capabilities, and yields more accurate results by combining both keyword and semantic information.
